GeoWave EMR Quickstart Guide: Jupyter Notebook
Assumptions
This document assumes you understand how to create and configure an EMR cluster for GeoWave. If you need more information on the steps involved in setting up a cluster to support GeoWave visit:
Configuring Spark
To better configure Spark for our demos we use an option provided by AWS to maximize the memory and CPU usage of our Spark cluster called maximizeResourceAllocation. This option has to be provided at cluster creation as a configuration option given to Spark.
For more information on how to set this option visit Configuring Spark.
|
Setting this option on some smaller instances with HBase installed can cut the maximum available yarn resources in half (see here for memory config per instance type). AWS DOES NOT account for HBase being installed when using |
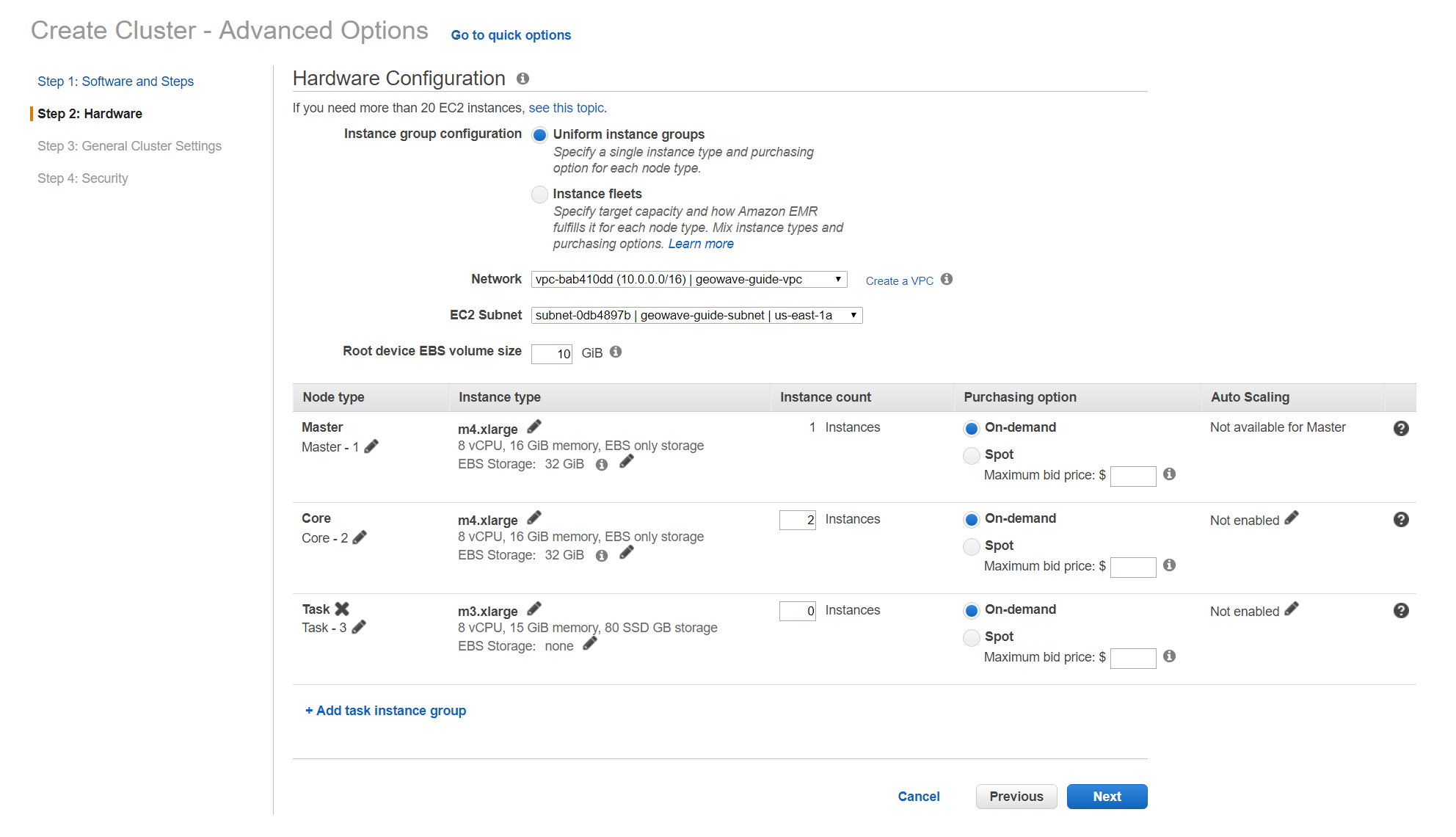
Recommended Hardware settings
Currently, there are two notebook demos using differently sized data sets. If you wish to run either jupyter notebook demo you will need to modify the hardware specifications of your emr cluster to at least the minimum required settings specified for the demos below.
Install Python and Jupyter
To properly run and visualize the results from the Jupyter notebook demo we need to first install python and a few additional packages. We’ve created a bootstrap script to do that for you that can be found here:
This bootstrap script will install Python, all necessary packages needed for the demos, create the Jupyter kernel, and run the Jupyter notebook server on port 9000 of your cluster. This script needs to be run as a bootstrap action when creating the EMR cluster.
|
It is recommended to use the Accumulo bootstrap script as the first bootstrap script to setup your cluster. Doing so will let you use both HBase and Accumulo as long as you select HBase as a default application (backed by S3) to add to your cluster from AWS.
For more information on setting up bootstrap actions visit this AWS Environment Setup Guide |
Connect to the notebook server
After your cluster has been created with the script above and is in the Waiting state, you are ready to connect to the notebook server and run the demo:

-
Use the master public DNS of the cluster like below in your browser to connect to the notebook server.
{master_public_dns}:9000 -
Enter the default password
geowaveto gain access to the notebooks. -
Then simply select the demo notebook you wish to run and follow the instructions in the notebook to proceed through the demo. You can run each cell of the notebook by pressing [SHIFT + ENTER] while a cell is in focus.
Appendices
Modifying Spark settings on Jupyter kernel
Our bootstrap scripts setup the Jupyter kernel to use yarn by default, and other Spark configuration settings through the kernel.json file for the kernel itself. If for any reason you would like to change these settings, you can do so by modifying the kernel.json once you are connected to the cluster.
-
SSH into the emr cluster
-
Open the
kernel.jsonfile in your favorite text editor (vim, vi, nano) found at the following location-
/home/hadoop/.local/share/jupyter/kernels/pythonwithpixiedust22/kernel.json
-
-
Modify
PYSPARK_SUBMIT_ARGSto contain whatever settings you need for spark. -
Restart the Jupyter Kernel (if running), or your settings will be applied the next time the kernel loads.
Restarting the Jupyter Daemon
The Jupyter notebook server is launched at cluster creation as a Upstart service. If Jupyter should stop working or need to be restarted after the cluster has been created, you can do so by following these steps.
-
SSH into the emr cluster
-
Run the following commands
sudo stop jupyter sudo start jupyter